Introduction:
Dow Jones USA completion total stock market index. Completion Total Stock Market Index is a benchmark for the overall performance of the U.S. stock market. It is designed to represent the broadest measure of the market, comprising all publicly traded stocks in the United States, including small, mid, and large cap stocks. This makes it an important tool for investors and traders who want to get a comprehensive overview of the market and track its movements.
Dow jones USA completion total stock market index is important for several reasons. First, it provides a snapshot of the market’s overall health and performance. By tracking the index, investors can gain insight into the market’s direction and make informed decisions about their investments. Additionally, the index can be used to gauge the performance of specific sectors or industries within the market. For example, if the index is rising, it may indicate that the overall market is performing well, which could be a good sign for investors.
What is the Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index?
Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index differs from the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) in that it includes a wider range of stocks. The DJIA is a price-weighted index that tracks the performance of 30 large, blue-chip stocks, while the Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index includes all publicly traded stocks in the U.S. market.
The components of the Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index are determined by Dow Jones Indexes, a unit of S&P Dow Jones Indices. The stocks included in the index are selected based on various criteria, such as liquidity, size, and sector representation. They are also weighted based on their market capitalization, with larger companies having a greater impact on the index value. This weighting system is designed to reflect the market’s overall composition and ensure that the index accurately reflects the performance of the market.Regenerate response
History of the Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index
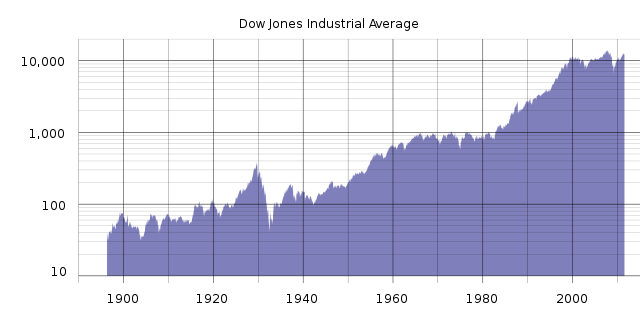
The index was developed by Dow Jones Indexes, a division of Dow Jones & Company, which was founded in 1882 by Charles Dow, Edward Jones, and Charles Bergstresser. The first Dow Jones index, the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), was created in 1896 and originally consisted of 12 stocks. Over the years, the DJIA has grown to include 30 stocks and has become one of the most widely followed and recognized stock market indices in the world.
In 2003, Dow Jones Indexes introduced the Dow Jones TSM Index as a complement to the DJIA. The Dow Jones TSM Index was designed to provide a more comprehensive measure of the U.S. stock market by including both large and small capitalization stocks, whereas the DJIA is limited to large capitalization stocks. The Dow Jones TSM Index includes all of the stocks in the DJIA as well as a wide range of additional stocks, making it a more representative measure of the U.S. stock market as a whole.
Since its inception, the Dow Jones TSM Index has undergone several changes. In 2011, Dow Jones Indexes implemented a new methodology for the index that included a number of changes to the way the index was calculated and weighted. In 2015, Dow Jones Indexes announced that it would be changing the name of the Dow Jones TSM Index to the Dow Jones U.S. Total Stock Market Index, to better reflect the scope of the index.
How the Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index is calculated
To calculate this Index, Dow Jones Indexes first selects the stocks that are eligible for inclusion in the index. These stocks are chosen based on various criteria, such as liquidity, size, and sector representation.
The selected stocks are then weighted based on their market capitalization, with larger companies having a greater impact on the index value.
The value of the Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index is determined by summing the market capitalizations of all the component stocks and dividing that number by a divisor.
The divisor is a figure that is used to adjust the index value for changes in the number of component stocks or for corporate actions such as stock splits or mergers.
There are several factors that can impact the value of the Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index. These include changes in the market value of the component stocks, shifts in investor sentiment, and economic events that affect the overall performance of the market.
For example, if the market value of a large component stock declines significantly, it could drag down the value of the index. Similarly, if investors become more optimistic about the market, the index value could rise.
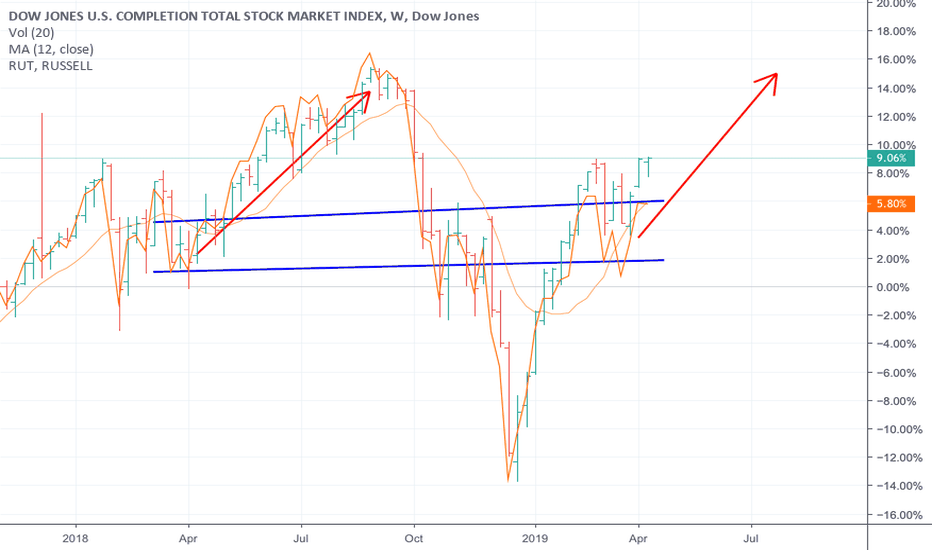
Using the Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index as a market indicator
One way to use the Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index as a market indicator is to track its movements over time. If the index is rising, it may indicate that the market is performing well, with stocks generally increasing in value.
On the other hand, if the index is falling, it may indicate that the market is struggling, with stocks generally decreasing in value. By tracking the index, investors and traders can get a sense of the market’s overall direction and make informed decisions about their investments.
The Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index is also often compared to other market indicators, such as the S&P 500 Index or the NASDAQ Composite Index. These indices track the performance of a different set of stocks and may offer a slightly different perspective on the market.
By comparing the Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index to other indices, investors can get a more comprehensive view of the market and gain insight into its overall performance.
Investing in the Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index
Another way to invest in the Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index is to buy futures or options contracts based on the index. These financial instruments allow investors to speculate on the future direction of the index or hedge their portfolio against market risk. However, trading futures and options carries additional risks and may not be suitable for all investors.
For investors looking to incorporate the Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index into their investment strategy, it is important to keep in mind that the index is a broad measure of the market and does not guarantee any specific level of performance. As with any investment, it is important to do your own research and consider your individual investment goals and risk tolerance.
Conclusion
In addition to its usefulness as a market indicator, the Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index is also an important tool for investors looking to gain exposure to the market. It can be accessed through various investment vehicles, such as index funds, ETFs, futures, and options contracts. By investing in these products, investors can participate in the market without having to buy individual stocks.
In summary, the Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index is a valuable resource for investors and traders looking to track the performance of the U.S. stock market and make informed investment decisions. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced investor, the Dow Jones U.S. Completion Total Stock Market Index can be a useful tool for understanding the market and maximizing your investment strategy.
Keep Following InveShares for more such awesome content right here!
FAQ :Dow Jones Completion Index
A: The Dow Jones Completion Index is a stock market index that tracks the performance of the small-cap and mid-cap stocks in the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA). It includes all of the companies in the DJIA, as well as a selection of smaller companies.
Q: What type of index is the Dow Jones Completion Index?
A: The Dow Jones Completion Index is a price-weighted index, which means that the value of the index is determined by the prices of the individual stocks it tracks, rather than their market capitalization.
Q: When was the Dow Jones Completion Index first established?
A: The Dow Jones Completion Index was first established on December 30, 1885, with a base value of 40.94.
Q: How is the Dow Jones Completion Index different from the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA)?
A: The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is a stock market index that tracks the performance of 30 large-cap stocks listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the NASDAQ. The Dow Jones Completion Index includes all of the companies in the DJIA, as well as a selection of smaller companies.
Q: What companies are included in the Dow Jones Completion Index?
A: The Dow Jones Completion Index includes all of the companies in the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), as well as a selection of smaller companies. The specific companies included in the index may change over time as the index is regularly reviewed and rebalanced.
Q: How is the value of the Dow Jones Completion Index calculated?
A: The value of the Dow Jones Completion Index is calculated by adding the prices of all of the stocks in the index and dividing the total by the number of stocks in the index. The resulting number is then multiplied by a divisor, which is used to adjust for any corporate actions such as stock splits or dividend payments.
Q: What is the base value of the Dow Jones Completion Index?
A: The base value of the Dow Jones Completion Index is the value of the index on its base date, which is December 30, 1885. The base value is used as a starting point for calculating the index’s value over time.
Q: How is the Dow Jones Completion Index used?
A: The Dow Jones Completion Index is used as a benchmark for the performance of small-cap and mid-cap stocks listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the NASDAQ. It is often used by investors to gauge the overall health of the stock market and to make investment decisions.
Q: How often is the Dow Jones Completion Index updated?
A: The Dow Jones Completion Index is updated in real-time during market hours. It is also reviewed and rebalanced on a regular basis to ensure that it accurately reflects the performance of small-cap and mid-cap stocks.
Q: Is the Dow Jones Completion Index the same as the S&P 500?
A: No, the Dow Jones Completion Index is not the same as the S&P 500. The S&P 500 is a stock market index that tracks the performance of 500 large-cap and mid-cap stocks listed on the NYSE and the NASDAQ. It is a market-capitalization-weighted index, which means that the value of the index is determined by the market capitalization of the individual stocks it tracks. The Dow Jones Completion Index, on the other hand, is a price-weighted index that tracks the performance of small-cap and mid-cap stocks listed on the NYSE and the NASDAQ.